For a company with Environmental, Health, and Safety concerns, there are two common types of environmental audits that are performed. Environmental management system audits help identify management system implementation gaps against a standard such as ISO 14001. Environmental compliance audits can be conducted against local and state regulations, but also against policies defined by government agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This article will focus on the use of audit protocols in managing environmental compliance audits.
The EPA published an Environmental Auditing Policy statement that encourages the use of environmental auditing by regulated industries in order to achieve and maintain compliance with environmental laws and regulation, and to help identify and correct unregulated environmental hazards[i]. To achieve this level of compliance, the EPA recommends the scope of an environmental audit to include a “systematic, documented, periodic, and objective review of facility operations and practices related to meeting environmental requirements”[ii].
An audit protocol is often used to develop and assign site-specific audit activities in order to evaluate their compliance within a range of requirements. The protocol will contain a variety of tools that can assist personnel with performing the audit. For example, the EPA protocol for conducting environmental compliance audits includes the following components[iii]:
- Guidance on key requirements
- Definitions of regulatory terms
- Overview of federal laws affecting a particular environmental management area
- Checklist containing detailed procedures for conducting a review of facility conditions
The last element, the audit checklist, is the actionable portion of the audit. Depending on the protocol requirements, responses to audit questions can range from simple “Yes/No” to complex scoring mechanisms with parent-child question relationships. Regardless of how questions are structured, many audit requirements are similar across organizations that perform environmental compliance audits. Three common elements of an environmental audit are:
- Records to review – management system documents, permits, hazardous substance records
- Physical features to inspect – facility tour, cleanup sites, disposal sites, manufacturing and processing equipment
- Interviews – Subject Matter Experts (SMEs), field-level employees, supervisors
Once an audit is completed, the audit protocol provides the framework for correcting deficiencies uncovered by the auditing team. Root cause analysis, which helps determine the underlying cause of a problem rather than focusing remediation of its symptoms, is often used as an investigation method to ensure that environmental problems don’t reoccur. Once the audit analysis is done, non-conformances are grouped into findings to be addressed through corrective action tasks.
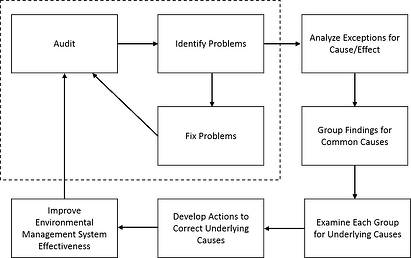
Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under the Stormwater Program, iv
When this process is adhered to, organizations can expect better compliance and overall environmental performance. The benefits can be cross-cutting throughout departments, business units or even company-wide. For example, if an opportunity to reduce energy consumption and reduce waste is identified from an audit at one facility the change could be implemented globally, allowing the company to lower cost overall.
Because of these benefits, the EPA encourages regulated entities to look at compliance as the floor, rather than the ceiling, of environmental performance by instituting voluntary audit programs[iv]. An efficient way of introducing this approach is through periodic self-assessments. Self-assessments provide the chance to “practice” for an audit and catch non-conformances before they become costly violations or cause harm to human health.
Finally, the role of software in this process is simple. Audit management software assists with the facilitation of audits, making them more streamlined and effective. An automated system allows the user to integrate different steps of the audit process—from preparation and scoping to generating an audit report within the app or via PDFs (use a pdf manager for additional functionality) — and manage them in one place. Whether audits are performed internally or by a third party, audit protocol management is vital to ensuring compliance and improving environmental management system effectiveness.
[i] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under CERCLA, ii
[ii] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits for Hazardous Waste Generators under RCRA, iii
[iii] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under CERCLA, v
[iv] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under the Stormwater Program, i
